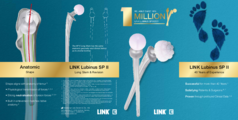
LINK SPII

Neutralizes torsional forces
The curved shape of the stem enables it to finds its way into the femoral canal, where it adapts perfectly to the anatomy.6 This means that stress peaks, as occur with three-point locking of straight shafts, are avoided and the stem has greater rotational stability.2
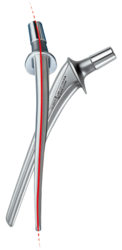
Developed in 1978, and available with a modular prosthesis head since 1984, this femoral stem was a great success and had a major influence on the principle of the anatomical hip prosthesis.1 The S‑shaped curvature, which follows the natural anatomy of the femur, has proved highly successful in this system. This has been repeatedly confirmed over the last 40 years in numerous publications, including the Swedish Hip Arthroplasty Register.1, 3 The outstanding clinical history was the reason for developing the ribbed prosthesis, the C.F.P. stem, and the SP-CL, based on the same principle.
Anatomical design
The anatomical shape of the stem enables it to fit centrally in the medullary canal. This helps to ensure a uniform cement coating, which can envelop the implant optimally.7 At the same time, anteroposterior and mediolateral ribs contribute to rotational stability.2, 8, 9, 10
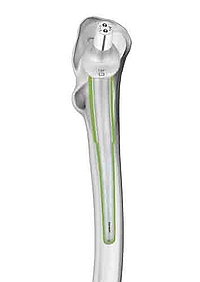
Optimal anatomical reconstruction
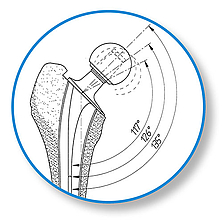
The SPII offers a system with great modularity. The multiplicity of possible variations in CCD angle, neck length, and stem length gives maximum flexibility for reconstruction of the anatomical structures in primary and revision arthroplasties. The stem tip is curved on the lateral side in order to prevent impacts when it is introduced into the medullary canal. The slender stem design meets all the requirements for minimally invasive, soft tissue, and bone-conserving implantation.
Successful long-term outcomes
Many long-term outcomes with survival rates of up to 92.3 percent after 23 years emphasize the success and great reliability of the SPII Stem.1
* www.odep.org.uk; Orthopaedic Data Evaluation Panel

- Kärrholm, Lindahl, Malchau, Mohaddes, Rogmark, Rolfson, ANNUAL REPORT 2015; The Swedish Hip Arthroplasty Register
- W.T. Stillwell. The Art of the Total Arthroplasty. Grune & Stratton, Inc. 1987; pp. 296
- H. Malchau et al; Prognosis of Total Hip Replacement, Orthopädie, Universität Göteborg, Schweden, 2002
- Malchau H, Herberts P, Ahnfelt L. Prognosis of total hip replacement in Sweden. Follow-up of 92.675 operations performed 1978-1990. Acta Orthop Scand 1993;64 (5): 497-506
- Garellick, Kärrholm, Rogmark, Rolfson, Herberts, ANNUAL REPORT 2014; The Swedish National Hip Arthroplasty Register.; p. 75
- Annaratone, Giovanni; Surace, Filippo Maria; Survival analysis of the cemented SPII stem; J Orthopaed Traumato (2000) 1:41-45. Springer Verlag
- LINK News Orthopädie aktuell, Spinger-Verlag GmbH & Co. KG, SPII® Modell Lubinus® - Stellenwert der SPII® Modell Lubinus® Hüftprothese im aktuellen Bericht des Nationalen Schwedischen Hüft-TEP-Registers von 1979 - 2002
- Langhans, M., Hofman, D., Ecke, H., & Nietert, M. (1992). Der Einfluß der Formgebung des Prothesenschaftes auf die Beanspruchung des proximalen Femurs. Unfallchirurgie, 18(5), pp. 266-273.
- Noble, P., Alexander, J., Lindahl, L., Yew, D., Granberry, W., & Tullos, H. (1988). The anatomic basis of femoral component design. Clinical Orthopaedics and Related Research(235), pp. 148-165.
- Denaro, V., & Fornasier, V. (2000). Fill, fit and conformation - an anatomical and morphometric study of a hip component in total hip arthroplasty (Rippen-Link). European Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery & Traumatology, 10(4), pp. 239-247.
- High risk of early periprosthetic fracture after primary hip arthoplasty in elderly patients using a cemented, tapered, polished stem: An observational, prospective cohort o study on 1,403 hips with 47 fractures after a mean follow-up time of 4 years· Broden C, Mukka S, Muren O, Eisler Stark A, Skoldenberg O, Acta Orthopaedica 2015; 86 (1):x-x