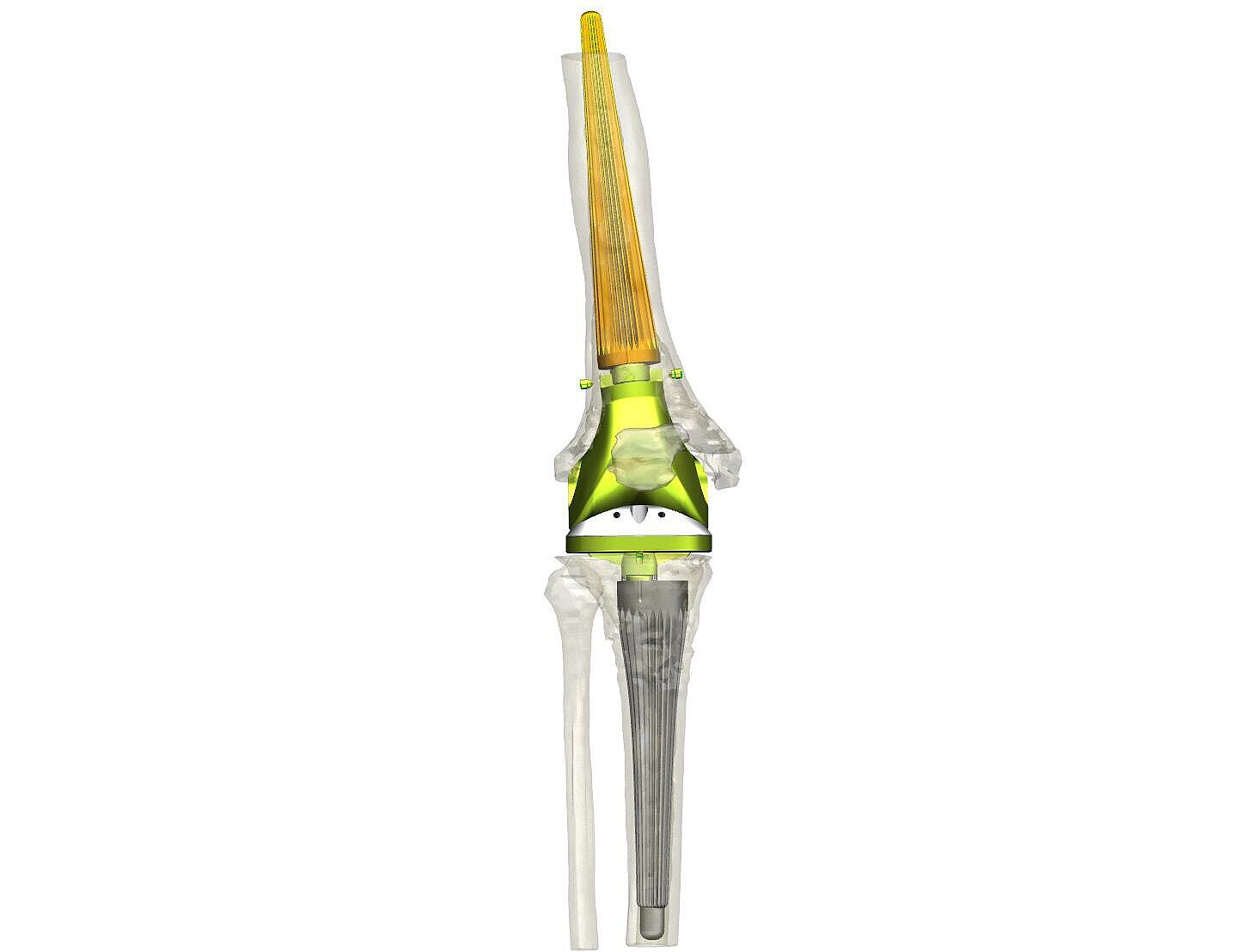
Patient Case Report: Rescue in Catastrophic Cases: Successful Knee Revision
Knee Revision in a 63-Year-Old Patient Using Short-Stem Modular Component
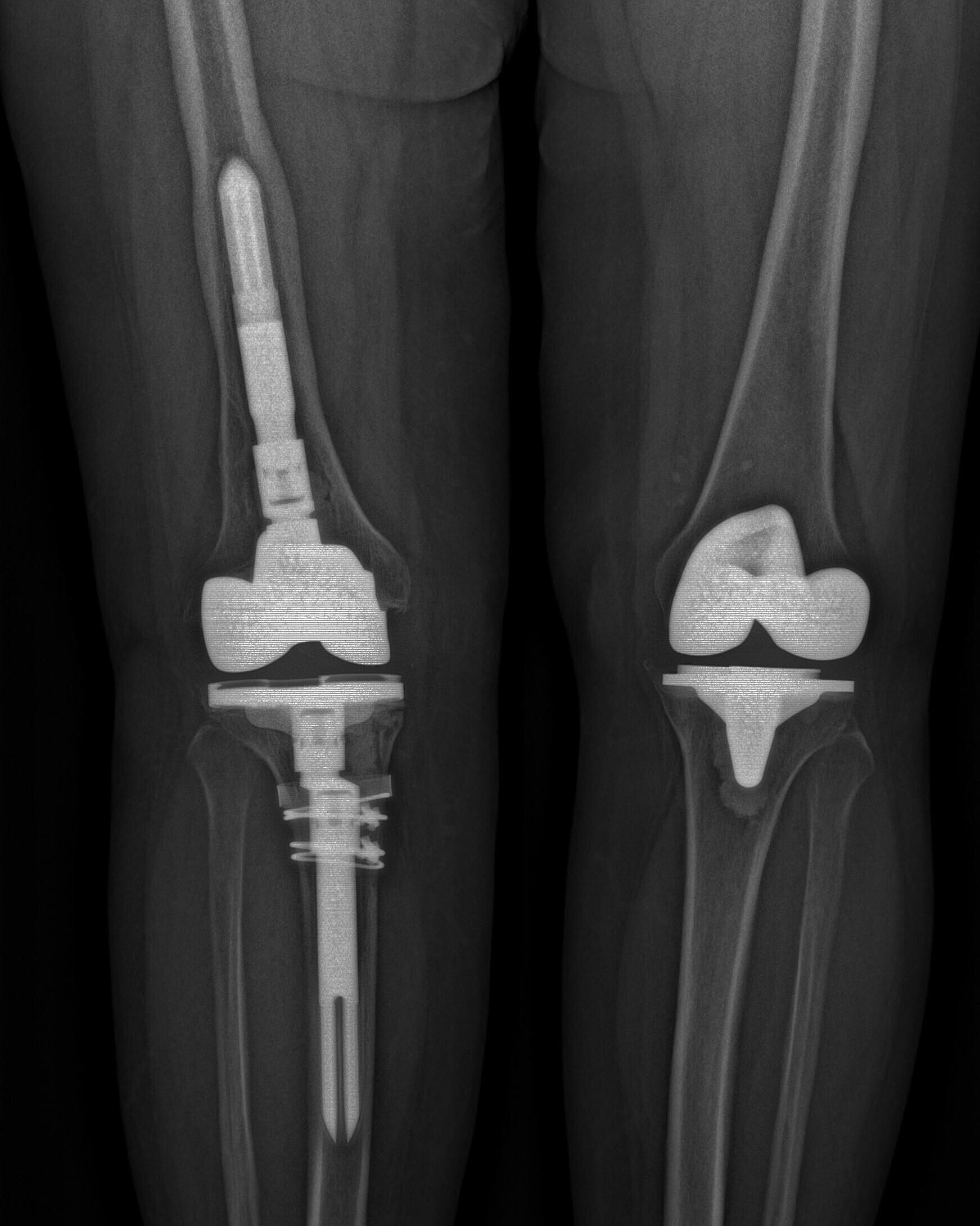
Image 1: Preoperative X-rays showing the original cemented knee prosthesis in situ; full-length anteroposterior view (left); medial view (right)
A 63-year-old female patient, measuring 168 cm in height and weighing 63 kg, presented with symptomatic aseptic loosening of the femoral component in the distal femur, accompanied by extensive bone loss. In addition to the mechanical failure, a clinically relevant nickel allergy
was identified, necessitating the use of implants with proven ion shielding. Given the combination of severe bone compromise, and material
sensitivity, a highly individualized surgical strategy was required. The surgical plan included a modular rotating-hinge knee revision using
components from the Endo-Model knee family/system.
Tailored Implant Strategy: Combining Standard and Custom Components
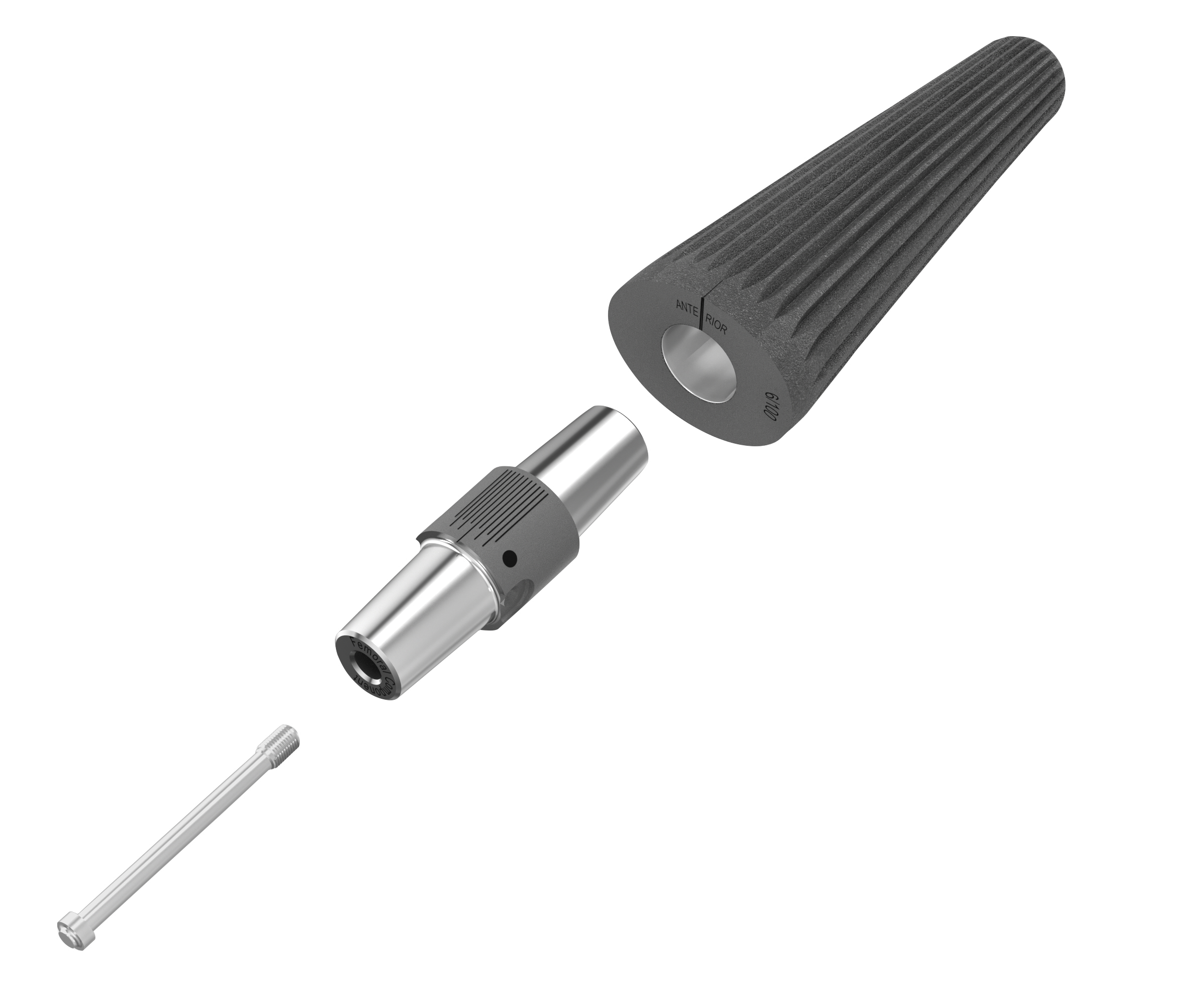
A slim distal femoral replacement (rotating version, size medium, width 65 mm) made of CoCrMo with a PorEx (TiNbN) coating was selected, connected via a 5 mm short adapter also coated with PorEx. A medium tibial component of the same system (CoCrMo, PorEx-coated, 10/12 taper) was matched to the femur.
Anchorage and Modularity: Distal Fixation with the Link OptiStem
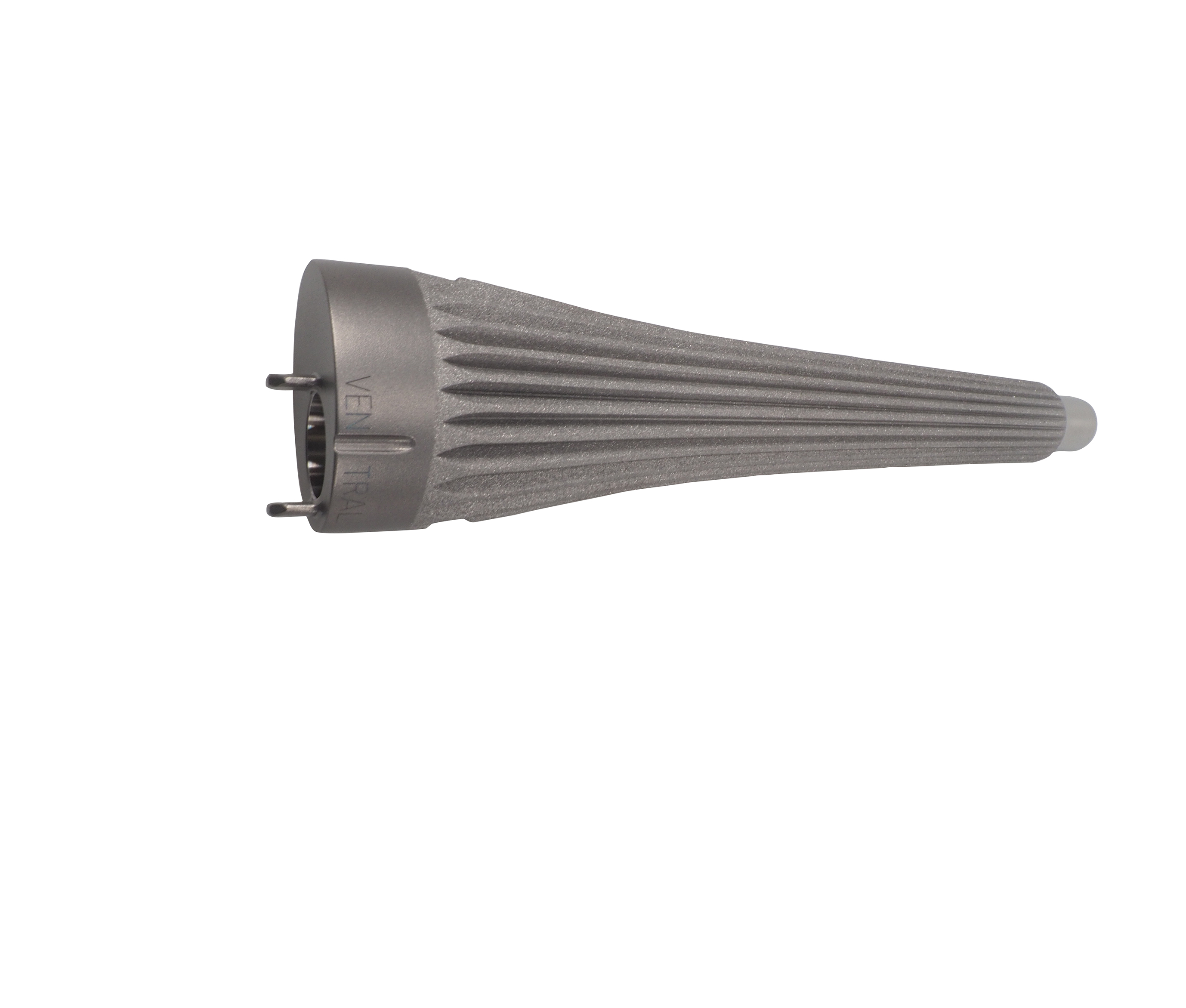
To address bone loss in the femur, the surgical team chose a curved, uncemented femoral stem from the new Link OptiStem portfolio. The
modularity of the system allowed precise rotational alignment, individualized stem length selection, and secure coupling via proven taper
connections. On the tibial side, a right-sided, anatomically curved, uncemented tibial stem (customLINK tibial OptiStem, Ti6Al4V, polished tip) was used. Tibial spacers in 5 mm and 10 mm height were also prepared for intraoperative adjustment.
Managing Sclerotic Bone: Technical Challenges in the Femur
The surgical approach was complicated by a severely sclerotic medullary canal in the distal femur, which rendered conventional reaming
ineffective. The team employed tapered reamers and a rose-head burr to remove dense sclerotic bone, allowing for controlled stem insertion and proper alignment. Only after meticulous debridement was adequate canal access achieved.
Intraoperative Decision-Making: Stable Fixation Despite Bone Loss
Trial implantation showed excellent axial and rotational stability, leading the team to proceed with a short femoral stem, which precisely
eplicated the trial positioning. The definitive implant components achieved immediate fixation, even in the presence of a large metaphyseal defect, confirming the viability of short-stem anchorage in high-risk geriatric patients.
The Optimal Stem Option: Flexibility and Reliability
The Link OptiStem provided multiple advantages: intraoperative freedom to choose between cemented (on request only) and cementless
fixation, free rotational adjustment via the adapter, and leg length balancing through the adapters and/or additionally different stem lengths.
The stem’s anatomical design—with distal metaphyseal press-fit, oval cross-section, and curvature adapted to the meta-/diaphyseal femur—ensured self-positioning and secure rotational stability.
Anatomical Self-Positioning: Designed for Femoral Fit
Developed based on decades of experience with custom implants and supported by published scientific data, the anatomical design of the Link OptiStems reflects the natural curvature of the anatomical femur. The result is self-positioning, enhanced feedback during instrumentation, and
a lumen-filling, oval stem profile that tapers to round distally, thereby reducing cortical stress.
Anchorage in the Restoration Zone: Secure and Bone-Conserving
Anchorage was achieved in the femoral restoration zone via distal press-fit mechanics, supported by the oval stem geometry and anatomical alignment. The system’s compatibility with the Endo-Model SL and the new LINK Endo-Model EVO further underscores its versatility across
generations of hinged knee systems.
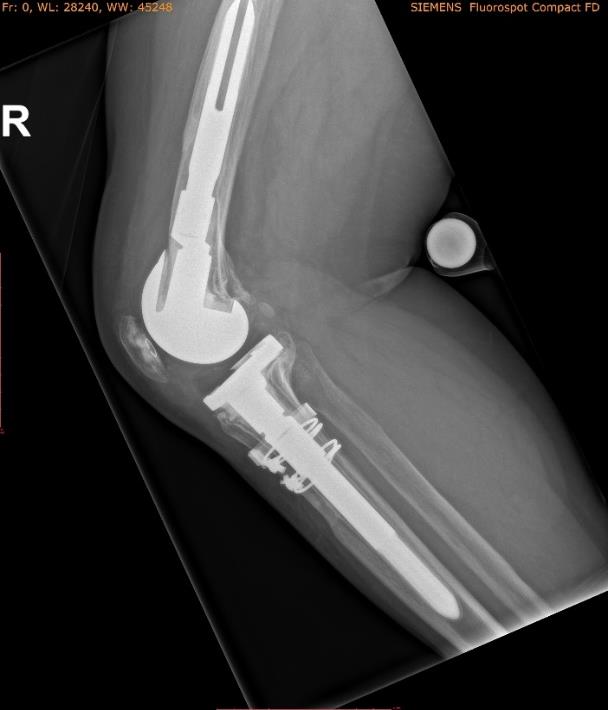
Postoperative Outcome: Functional Stability with Minimum Invasiveness
The final construct—comprising a PorEx-coated, rotating-hinge LINK Endo-Model EVO-W knee prosthesis combined with anatomically aligned short-stem fixation—provided robust mechanical stability and full compatibility with the tibial component in situ. The patient benefited from a bone-preserving, immunologically sound solution despite the significant bone deficit.
Rescue Plan Readiness: Engineered for the Unexpected
The implant system incorporated a pre-defined fallback strategy, including cementless meta-/diaphyseal fixation via an anatomically curved, oval, tapered femoral stem and modular revision compatibility. This rescue-ready concept ensured intraoperative flexibility even under challenging conditions.

More information about Link OptiStems can be found via
www.link-ortho.com/products/knee/link-optistem