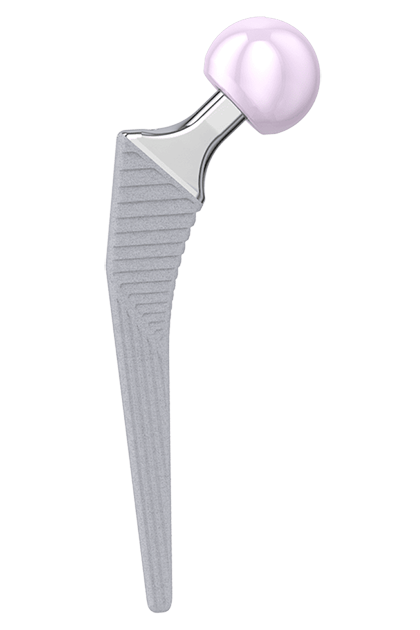
The LCU Hip System offers an uncemented hip stem with an HX coating. The design follows the concept of a straight stem with tapered lateral shoulder. The profile is straight with a rectangular cross-section.
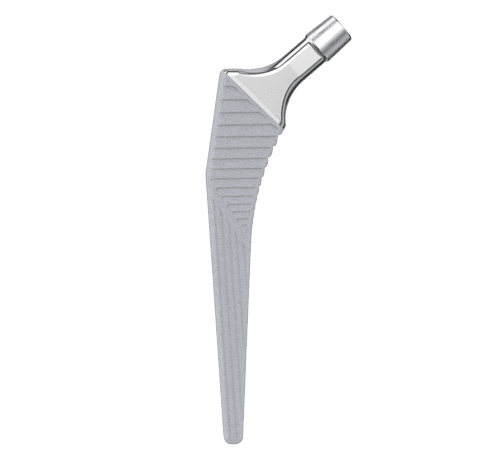
Two offset types allow for adaption to the patient’s anatomy 2:
- Standard type with a CCD angle of 130º
- Lateralizing type with a CCD angle of 125º
The stability of the implant is additionally enhanced by the characteristic metaphyseal V-shape, while the rectangular cross-section neutralizes torsional forces.5, 6, 8
Meta-diaphyseal support and fixation provided by a large medial curvature with a 100 mm radius for anatomical adaptation, prerequisite for primary and secondary stability.


The flat, tapered prosthesis neck allows a large range of motion between prosthesis stem and acetabular cup.2
The 12/14 mm taper is designed for the use of modular LINK prosthesis heads made of ceramic or metal with various lengths and diameters.
Furthermore, the highly polished neck region reduces abrasion in the event of unintentional contact with the acetabular cup.9
Uncemented Version
The stem is made from Tilastan-S (Ti6Al4V).
The micro-roughness of the metal surface is created by corundum-blasting, which produces an even and uniform surface structure.
The HX coating with a thickness of 20 +/- 10 µm is applied by LEP (LINK Electrochemical Process) to the entire length of the prosthesis stem.
The horizontal ribs in the proximal section of the stem serve to counteract subsidence of the stem and to promote primary stability. The distal region has vertical ribs to counteract the rotational forces.7

Sources
- General information on Corail-type femoral stems: Hallan, G., et al. "Medium-and long-term performance of 11 516 uncemented primary femoral stems from the Norwegian arthroplasty register." Bone & Joint Journal 89.12 (2007): 1574-1580."
- Internal documentation W. LINK
- Garcia-Rey E, Garcia-Cimbrelo E. Grit-Blasted Implant Bone Interface in Total Joint Arthroplasty. In: Karachalios T, editor. Bone-Implant Interface in Orthopedic Surgery: Basic Science to Clinical Applications. London: Springer; 2014. p. 83-9.
- Yang C., Effect of calcium phosphate surface coating on bone ingrowth onto porous-surfaced titanium alloy implants in rabbit tibiae, J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2002 Apr;60(4):422-5.
- Hwang KT, Kim YH, Kim YS, Choi IY. Total hip arthroplasty using cementless grit-blasted femoral component: a minimum 10-year follow-up study. The Journal of arthroplasty. 2012;27(8):1554-61.
- Jones DL, Westby MD, Greidanus N, Johanson NA, Krebs DE, Robins L, et al. Update on Hip and Knee Arthroplasty: Current State of Evidence. Arthritis care & research. 2005;53:772-80.
- Vidalain, Jean-Pierre. Twenty-year results of the cementless Corail stem. International orthopaedics, 2011, 35. year, No. 2, p. 189-194.
- Khanuja H, Vakil J, Goddard M, Mont M. Current Concepts Review: Cementless Femoral Fixation in Total Hip Arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2011;93:500-9.
- International Orthopedics, Volume 41, Number 3, March 2017, Page 611-618
- (Scheerlinck, T., and P-P. Casteleyn. "The design features of cemented femoral hip implants." Bone & Joint Journal 88.11 (2006): 1409-1418.)